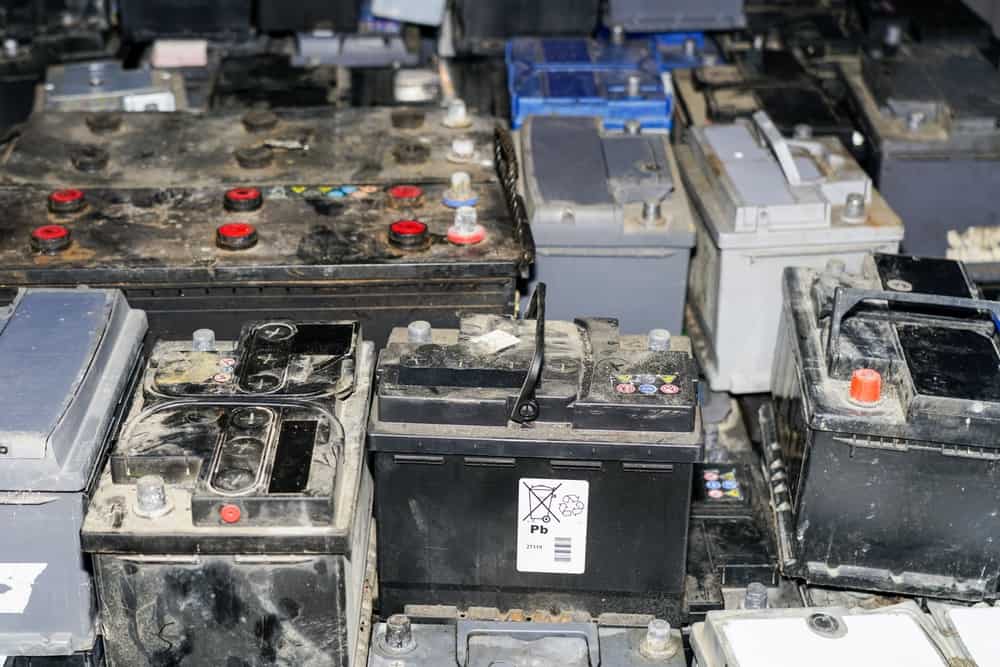
Lead batteries account for the top recycled consumer product in the United States. Their recycling rate is at an impressive 99.3%, which means landfills are spared from 1.7 million tons of batteries each year.
This level of recycling efficiency demonstrates the industry’s investment in an aggressive lead battery recycling system. The legal repercussions of throwing lead batteries in the trash also encourage people to send their used batteries to recycling centers.
In case you didn’t know, disposing of lead batteries in garbage bins is illegal because these materials contain harmful substances. Despite new battery technologies, lead batteries have potential environmental contaminants. They pose an array of health hazards for communities and wildlife. As such, their life cycle requires them to join the recycling loop.
How are Lead Acid Batteries Recycled?
The process involves a stringent method for how lead batteries are recycled. It consists of the following steps:
1. Lead Battery Breaking and Separation
Recycling plants receive truckloads of scrap batteries, which first go through a breaking and separation system. Next, an industrial hammer crushes the scrap batteries with the crushed parts passing through a sieve conveyor for cleaning. The conveyor also separates the lead oxide powder from the rest of the battery components.
Upon the separation of the lead oxide, sink and float tanks receive the crushed parts. The last tank separates the plastics, such as polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE), from the lead.
2. Desulfurization
The desulfurization process removes the sulfur dioxide content from the lead paste through the addition of sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, or ammonium bicarbonate.
First, the lead paste is collected from the last tank used in the breaking and separation process. It then goes to a reaction tank where the reagent is added to induce the desulfurization process.
Afterward, the resulting lead slurry is pumped to the filter press for dewatering, then discharged into a dedicated container to prepare it for smelting.
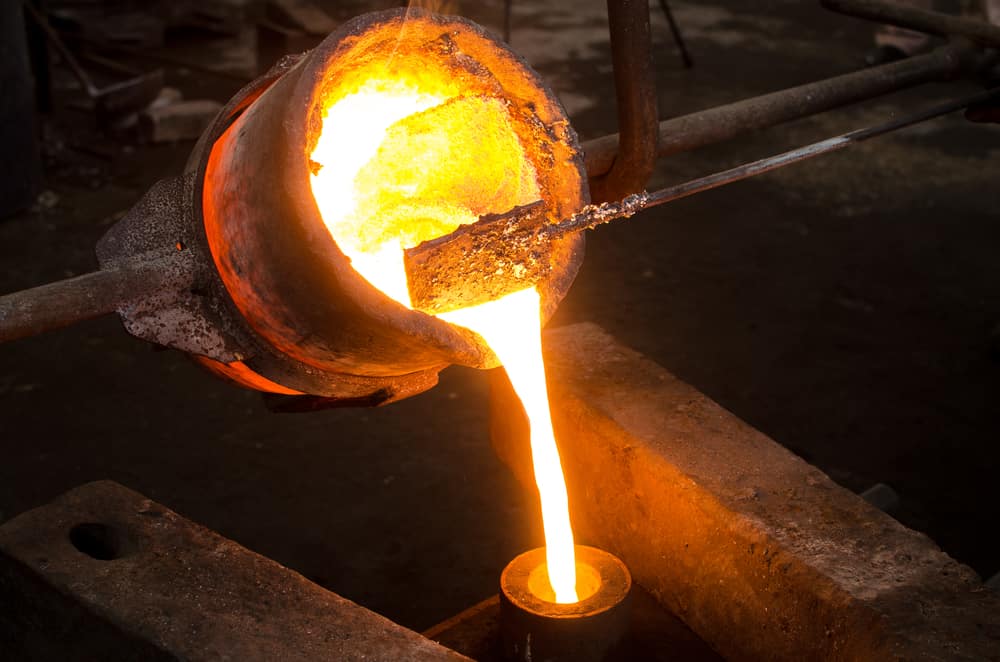
3. Lead Smelting
Smelting involves separating impurities from the metal through heating. The slurry is placed in a furnace capable of high temperatures to produce molten lead.
This step requires reliable heating equipment, such as rotary furnaces. Compared to a stationary furnace, a rotary furnace allows high utilization of input energy. The equipment limits the volume of off-gases by utilizing oxy-fuel burners. The design of a rotary furnace renders it highly compatible with lead acid battery recycling.
4. Lead Refining and Alloying
The product of smelting via a rotary furnace is called hard or crude lead. Hard lead still contains residual oxides and toxic slag, requiring further processing. Through stirring, the impurities that collect at the surface are skimmed off.
Compared to a blast furnace, smelting lead using a rotary furnace produces less contamination and unwanted by-products. That’s a major consideration given how battery manufacturing requires soft lead with 99.97% purity. Tin and antimony are sometimes added to achieve the desired grade of hard lead.
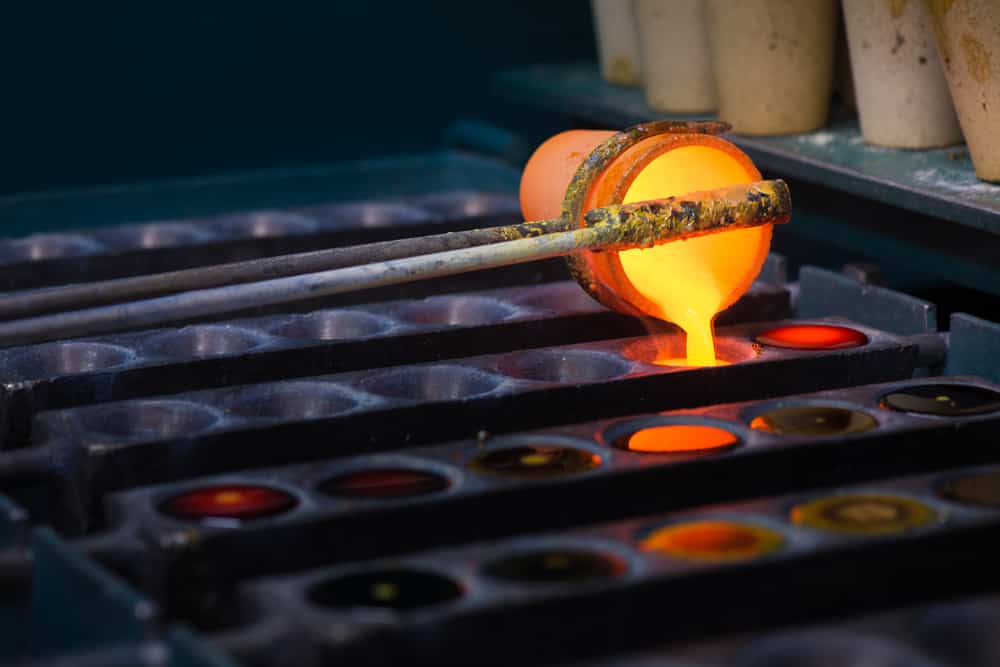
5. Lead Casting
The last step entails using a casting machine composed of chain conveyor mechanisms. Pure lead is poured into the molds through a lead pump or flow regulating valves. The lead will then solidify into ingots.
The ingot stacking process follows lead casting. The lead ingots are stacked together using forklifts until they’re ready to be shipped to manufacturers, factories, and assembly lines.
How are Rotary Furnaces Used for Battery Recycling?
In the battery recycling process, rotary furnaces are primarily used for smelting. They’re ideal for melting down lead into its purest state because their design allows for higher energy input compared to stationary furnaces. This type of furnace also comes with air pollution control system attachments that capture flue gasses and other by-products, preventing them from getting released into the facility’s environment.
Other than smelting, you can also use rotary furnaces for further treating and recovery of by-products, such as slag. This makes rotary furnaces more efficient than blast furnaces, which are typically used for battery recycling, since the latter can’t process lead slag.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/rotary-furnace
Why Use Rotary Furnaces to Recycle Lead Batteries?
The smelting process in lead battery recycling can be done using various equipment, such blast and stationary furnaces. However, in terms of reliability, industry stakeholders trust rotary furnaces.
Here’s what makes rotary furnaces superior to other types of furnaces when it comes to battery recycling:
-
Rotary furnaces offer higher production capacity, meaning you recover more lead per operation cycle. As a result, you not only save time but also maximize resources. This approach is excellent for increasing your profit margin.
-
Rotary furnaces are user-friendly. They are easy to operate, so relatively unskilled workers can man them. You do not require a lot of manpower, which lets you save on labor. The equipment’s ease of use also results in faster product delivery with fewer instances of error.
-
Rotary furnaces are versatile. On top of battery scraps, they can also process baghouse powder, blast furnace waste, and lead ores. That means your processing plant can venture into other modes of production should you want to expand your manufacturing capacity.
Rotary Furnaces for Lead Battery Recycling
Lead battery recycling achieves two objectives: reducing raw material harvest and eliminating lead batteries in landfills. The second one is of utmost concern, given how battery research has shown that the two main components of lead batteries – lead and sulfuric acid – are dangerous to the environment and human health.
Here, it’s vital to prioritize how batteries are made and how they are recycled. For the latter, it’s best to include rotary furnaces in your system. You cannot rely on substandard equipment considering the risks involved.
For top-caliber rotary furnaces, check out Across International. Across International is an ISO-certified industry leader in lab equipment manufacturing and distribution, specializing in heat treatment and material processing.
Request a quote today on our rotary furnaces and other lab equipment.