Foundry Furnaces- Understanding the different methods and systems
Foundries are industrial production facilities specializing in metal casting. The main objective of the foundry is to melt metals, pour them into molds, and then solidify it to get solid metal parts, in the desired shape, and often with enhanced mechanical properties. Foundry furnaces are highly specialized types of heat treatment systems engineered to perform foundry process, and their operation plays a significant role in the transformation of raw materials into pure high quality usable components for research, engineering, and industrial applications. The melting rate, quality of the product, cost, and overall efficiency depend on the type of furnace used. Therefore, an understanding of heat, working principles, and material compatibility are important for metallurgical design, alloy production, and maintaining the quality of the product.
Types of Foundry Furnaces
Based on their engineering design, energy source, and working principle, foundry furnaces can be categorized into different groups. The below will provide more insight into the most common types of foundry furnaces
Cupola furnace
The cupola furnace is a widely used traditional metallurgical furnace particularly designed for melting cast iron. It is a vertical cylindrical furnace made from stainless steel and internally lined with refractory bricks to withstand the high temperatures generated during furnace operation. This type of furnace works on the principle of counter current heat exchange, where the solid metal charge moves downward while the hot combustion gases rise upward, ensuring efficient heat transfer and uniform melting.
A coke (form of carbon) is used as an energy source to melt cast iron by burning coke via combustion. Its operating temperature ranges from ~1500–1850 °C, making this type of furnace very popular in mass production of cast iron parts such as pipes and engine blocks.
Crucible furnace
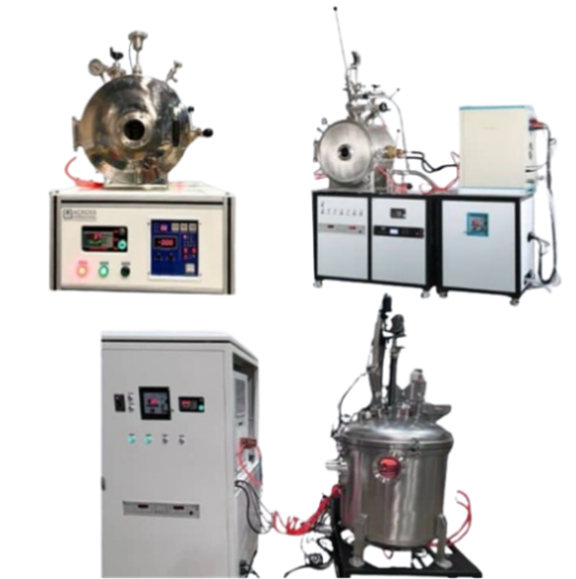
This furnace is used to melt metals and cast those for low melting points such as aluminum, brass, and bronze. It consists of a crucible made from heat resistance materials like tungsten, graphite, molybdenum, or ceramic, which can withstand high temperatures. The metals are melted inside the crucible where the melt is isolated from direct contact with the heating element, by use of the crucible, protecting the molten metal from contamination. This is an indirect heating method where heat energy is transferred to the crucible via conduction and radiation from the heat source. The metal inside the crucible melts due to the heat absorption through the crucible wall, and the molten metal is then poured into the molds for casting. Operating temperatures generally range from ~ 1200-1800°C. These types of furnaces are simple and cost effective, ideal for small batches, and compatible with non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, titanium, bronze, copper etc. Their simplicity and low cost make them ideal for small operations, while high-performance crucibles allow consistent melting with minimal contamination. Here are some examples of crucible furnaces offered by Across International for melting metals in a controlled vacuum and argon atmosphere.
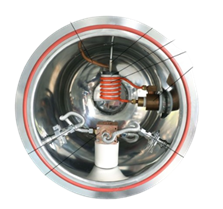
Electric ARC furnaces are important components in melting metals and steel production. An electric ARC is used to generate heat for melting metals. These furnaces work by creating an ARC between metal and graphite/tungsten electrodes, which produce extremely high temperatures to melt metals and alloys. Across International offers some electric ARC furnaces for melting refractory metals under high purity inert gas or vacuum conditions with different chamber dimensions and can be customized based on the customer’s demand. Below is an example of one of the Across International Electric AC furnaces for melting and casting various refractory metals.
Figure: Ai-Vacuum ARC furnace
It consists of a high frequency non-contact ARC system to generate a stable concentrated high temperature ARC, water cooled horizontal cylindrical vacuum chamber, vacuum pumping system, gas purging atmosphere, water cooled copper crucibles etc. They can reach up to 3000°C, allowing for fast melting and reducing energy waste compared to fossil fuel-based furnaces. Electric furnaces are known for being energy efficient, easy to operate, and environmentally friendly, making them a perfect choice in eco-friendly manufacturing.
The Induction furnace is an advanced piece of industrial equipment used to heat and melt metals via electromagnetic induction. It consists of a non-conductive crucible such as silica, zirconia, magnesia, or alumina, which is then surrounded by an induction coil. These types of furnaces are more energy efficient and ensure cleaner and environmentally friendly operations. A high frequency AC current flows through the coil; this generates a changing magnetic field in and around the coil. This magnetic field penetrates the metal placed inside the crucible and induces eddy currents in the metal. Due to the electrical resistance of the metal, these eddy currents generate heat and as a result the metal melts and circulates naturally due to electromagnetic string. Its operating temperature generally ranges from ~ 600-2000°C, depending upon the design and application, making it ideal for the controlled melting of ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Induction furnaces are widely used in industries that require high quality homogenous melts such as aerospace alloy production, laboratory metallurgy, and much more.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) and the role of vacuum
Vacuum induction melting is an advanced form of induction melting designed to produce high quality metal melts. The heating mechanism VIM is the same as standard induction furnace, but the main difference is that the melting process takes place inside a vacuum atmosphere, i.e. a vacuum chamber.
In the Vacuum induction melting, the presence of oxygen, moisture, and other gases are removed to prevent them reacting with molten metals. Vacuum atmosphere is crucial for the alloys containing reactive elements such as magnesium, aluminum, titanium etc. that oxidize quickly at high temperatures. Therefore, by removing these contaminants, vacuum induction melting ensures cleaner melting, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties and high purity. There is no heat loss with the surrounding air, which makes induction heating more uniform and maintains uniform temperature distribution resulting in enhanced stability and melting efficiency. For controlled casting, the furnace also can be backfilled with inert gas. Additionally, vacuum melting allows you to remove unwanted dissolved gases from the melt and reduce the oxidation of sensitive alloy elements. This makes vacuum induction melting an ideal technique for producing titanium alloys, nickel based super alloys, premium grade steel, and other metals used in applications such as medical implants and aerospace.
Figure: Ai-Vacuum Induction Melting furnace
Conclusion
Foundry furnaces are important industrial tools that enable the melting and casting of metals into high quality parts. To meet distinct metallurgical requirements, each type of furnace is designed with specific heating mechanisms and working principles. The cupola furnaces are designed for large scale melting of cast iron due to its economic operation. Crucible furnaces are engineered for low cost, simple, and indirect heating for small batch melting of non-ferrous metals. Electric ARC furnaces generate high temperatures through ARC discharge, making them a promising solution for melting and casting refractory metals under controlled atmosphere such as inert gas or vacuum. Additionally, induction furnaces use electromagnetic induction, and VIM combines the induction heating with vacuum, making it one of the most reliable techniques for producing clean and high-performance metal alloys. VIM technology plays a significant role wherever material consistency and purity are important. These furnaces form the foundation of modern foundry operations, enabling industries to customize melting processes for efficiency, alloy quality, and production volume.
FAQ:
1. What is a foundry furnace?
A foundry furnace is a highly specialized piece of industrial equipment used to melt metals so they can be poured into molds and shaped into finished parts. The furnace type directly impacts melting speed, metal quality, energy efficiency, and production cost.
2. Why are foundry furnaces important in the casting process?
Foundry furnaces provide the controlled heat needed to turn solid metal into a clean, uniform melt. This is essential for achieving strong mechanical properties, consistent casting quality, reliable alloy performance, and efficient manufacturing.
3. What factors determine which type of furnace is used?
The best furnace depends on:
- Metal melting temperature
- Required product quality
- Batch size and production volume
- Energy consumption goals
- Whether a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere is needed
- Budget and operational scale
4. Which furnace is best for melting non-ferrous metals?
Crucible furnaces and induction furnaces are ideal due to their clean melting environments and precise temperature control.
5. Which furnace is best for high-melting-point refractory metals?
A vacuum or inert-gas Electric Arc Furnace is the top choice because it can reach temperatures around 3000°C while maintaining metal purity.
6. Which furnace is the most economical for large-scale cast iron melting?
The cupola furnace is the most cost-effective solution for high-volume iron melting due to its low operating cost and high throughput.
7. Which furnace provides the cleanest and most energy-efficient melt?
Induction furnaces offer the cleanest melt with excellent temperature uniformity, high efficiency, and minimal emissions.
8. Why are foundry furnaces essential to modern manufacturing?
Foundry furnaces allow manufacturers to tailor melting conditions for specific metals, improve alloy performance, increase energy efficiency, and maintain strict quality standards. They form the backbone of modern metal casting and industrial production.