We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Tube Furnaces: Understanding the Differences for Industrial Heating Applications

In the realm of laboratory work, precision, and efficiency are paramount. Laboratory furnaces, with their ability to generate controlled and consistently high temperatures, play a vital role in numerous industries. They are indispensable tools for processes such as heat treatment, sintering, and materials research. In the realm of furnace configurations, vertical and horizontal furnaces hold prominent positions, each offering distinct features and advantages.
This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of vertical and horizontal tube furnaces, offering valuable insights into their distinctions and examining their impact on various applications. Whether you're a researcher, engineer, or technician, this exploration will deepen your understanding and empower you to make well-informed decisions for your laboratory pursuits. Join us as we unravel the nuances of vertical and horizontal furnaces and embark on a journey of heating excellence.
Vertical Tube Furnaces
Definition and Design: Vertical tube furnaces are characterized by their vertically oriented heating chamber or tube. Inside the tube, the sample or material to be heated is placed and subjected to the desired temperature. These furnaces feature a heating element surrounding the tube, facilitating efficient heat transfer and ensuring uniform temperature distribution along the sample's length.
Applications: Industries such as materials research, chemistry, and nanotechnology commonly employ vertical tube furnaces. They excel in processes like thermal decomposition, pyrolysis, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and annealing of materials. These furnaces are particularly advantageous for experiments that require precise temperature control and uniform heating of long or vertically aligned samples.
Advantages: Their vertical design simplifies the loading and unloading of samples, making batch processing convenient. Moreover, they provide excellent temperature uniformity along the tube's length, resulting in consistent and reliable outcomes. Additionally, vertical tube furnaces have a compact footprint, making them suitable for laboratories with limited space.
Limitations: However, it is crucial to remember that vertical tube furnaces have a smaller working capacity than their horizontal equivalents. This constraint may limit the amount or quantity of samples that may be processed at the same time.
Horizontal Tube Furnaces
Definition and Design: A horizontal tube furnace is a furnace with a horizontally oriented heating chamber or tube. The sample or material is placed inside the horizontal tube, and heat is applied to achieve the desired temperature. These furnaces typically feature a heating element that surrounds the tube, ensuring efficient heat transfer and uniform temperature distribution along the length of the sample.
Applications: Horizontal tube furnaces find applications in industries such as materials science, metallurgy, and ceramics. They are commonly used for processes including heat treatment, sintering, annealing, and thermal analysis. Horizontal tube furnaces are well-suited for handling larger sample sizes, multiple samples, or continuous production processes.
Advantages: One of the main advantages of horizontal tube furnaces is their larger working volume, which allows for processing of larger samples or multiple samples simultaneously. They provide flexibility in sample loading and unloading, making them suitable for batch or continuous production. Horizontal tube furnaces also offer excellent heat distribution along the sample, resulting in uniform heating.
Limitations: A limitation of horizontal tube furnaces is their larger footprint, which requires more space compared to vertical tube furnaces. The horizontal orientation may introduce slight temperature variations along the length of the sample, necessitating careful optimization of temperature profiles. Additionally, the handling and manipulation of samples within the horizontal tube may be more challenging compared to vertical tube furnaces.
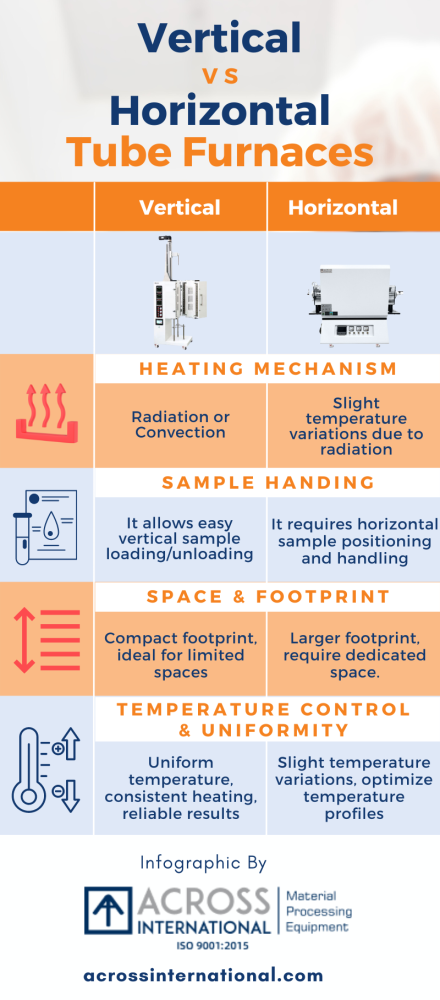
Key Differences between Vertical and Horizontal Furnaces
Heating Mechanism:
The heating mechanism in vertical and horizontal tube furnaces differs in terms of heat distribution and transfer. In vertical tube furnaces, the heating element surrounds the tube, ensuring efficient heat transfer through radiation or convection. This design facilitates uniform temperature distribution along the length of the sample. In contrast, horizontal tube furnaces also employ a heating element surrounding the tube, but heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation. This can result in slight temperature variations along the length of the sample.
Sample Handling:
Vertical and horizontal tube furnaces have different approaches to sample loading and positioning. In vertical tube furnaces, samples are typically inserted vertically into the tube. This allows for easy loading and unloading, especially for longer or vertically aligned samples. Horizontal tube furnaces, on the other hand, require samples to be positioned horizontally within the tube. This may involve more complex handling and positioning mechanisms, especially when dealing with larger or multiple samples.
Space and Footprint:
The space requirements and installation considerations for vertical and horizontal tube furnaces vary. Vertical tube furnaces generally have a more compact footprint, making them suitable for laboratories or facilities with limited space. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or placed on benchtops. Horizontal tube furnaces, due to their horizontal orientation, typically occupy more space. They may require dedicated floor space or additional infrastructure to accommodate their larger footprint.
Temperature Control and Uniformity:
Temperature control and heat distribution differ between vertical and horizontal tube furnaces. Vertical tube furnaces provide excellent temperature uniformity along the length of the sample due to the vertical orientation and the surrounding heating element. This ensures consistent heating and reliable results. Horizontal tube furnaces, while still capable of maintaining uniform temperatures, may experience slight temperature variations along the length of the sample due to the horizontal orientation. Careful optimization of temperature profiles may be required to ensure uniform heat distribution.
Industry-Specific Considerations:
Consider any industry-specific requirements or standards that may influence your choice. Different industries may have specific regulations or preferences regarding Laboratry furnace orientation, heating mechanisms, or temperature control. Consider the recommendations or guidelines relevant to your field.
The choice between vertical and horizontal tube furnaces relies on a careful evaluation of your specific needs and requirements. Understanding the differences in design, heating mechanisms, sample handling, space considerations, and temperature control is crucial for making an informed decision.
Across International is a trusted manufacturer of muffle furnace,induction heaters,vacuum ovens and Lab furnaces. Our specialized equipment ensures the safe handling of hazardous materials and maintains chemical purity. With meticulous design and a commitment to excellence, we offer tailored solutions for optimized laboratory processes. Contact us to elevate your lab with high-quality equipment and enhance research outcomes, and also learn more about our ISO 17025 Calibration Services.